| Name ____________________________ # _____ |
Section ________ |
|
Date __________ |
|
|
Extended Response Homework |
|
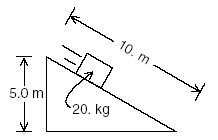
| Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the information and diagram below. The diagram below is provided for practice purposes only. Be sure your final answer appears on your answer paper. A ray of monochromatic light of frequency 5.00 × 1014 hertz is incident on a mirror and reflected, as shown. | |
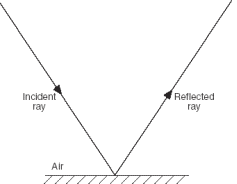 |
1.
Using a protractor and ruler, construct and label the normal to the
mirror at the point of incidence on the diagram on your answer paper.
[1] 2. Using a protractor, measure the angle of incidence to the nearest degree and record the value on your answer paper. [1] 3. Determine the wavelength of the ray of light. [Show all calculations, including the equation and substitution with units.] [2] |
| 4. What is the color of the ray of light? [1] | |
Base your answers to questions 5 through 6 on the information below. A
0.12-meter-long electromagnetic (radar) wave is emitted by a weather
station and reflected from a nearby thunderstorm.
|
|