![]()
![]()

Satellite Motion
|
Provide three examples
Communication:
Satellites enable global communication by transmitting signals
for television, radio, internet, and phone services across vast
distances. Weather Forecasting:
Satellites monitor weather patterns, track storms, and gather
data to predict weather conditions and natural disasters. GPS and Navigation: Satellites provide precise location and timing information, essential for navigation systems in cars, airplanes, and smartphones. |
I. Satellite Motion
Satellite - smaller body revolving around a larger body
Why Doesn't the Moon
Fall Down?
Resource produced by WGBH
and funded by the National Science Foundation.
![]() Teacher
Domain Discussion Questions
Teacher
Domain Discussion Questions
- Why doesn't the Moon hit Earth even though it is "falling" toward it?
- What would happen if the Moon moved faster than it does now?
- How is the Sun able to have so many planetary bodies in orbit around it?
- Why do planets closer to the Sun than Earth not fall into the Sun from the pull of gravity?
- If someone asked you if it's true that the Moon is always falling towards the Earth, what would you tell them?
Intro to Gravity - Flash
showmethephysics.com
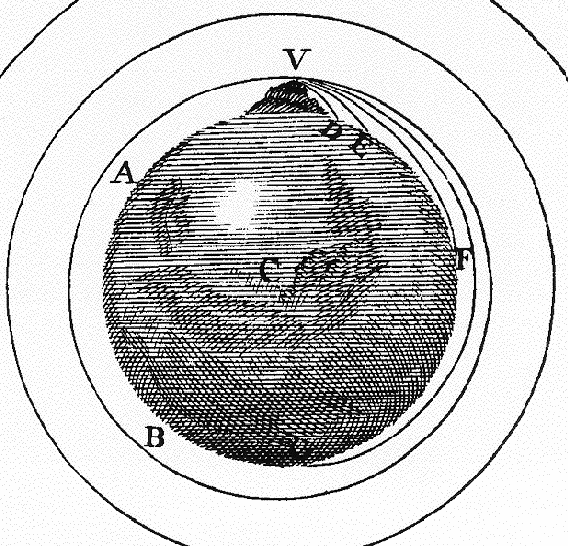
Illustration from Newton's
Principia
- Cannon on a Mountain
Natural Satellites

ex) Moon, all 8 planets, comet
Artificial Satellites
- weather, spy, communications
See where
the earth's
satellites are right now!
Click this link and wait until
the program jumps to the screen.
A. Satellite Motion
1. To send artificial satellite in circular orbit around earth it must first achieve a speed of 7900 m/s
If greater than 7900 m/s satellite has an elliptical orbit
If velocity is greater than 11 km/s then satellite leaves earth's orbit (called escape velocity)
2. Air resistance slows down satellites and eventually causes them to spiral back to earth.
Meteorite Peekskill, Ct. (NASA)

![]()
Winslow, Arizona
Crater created when a 50-meter-wide (160-foot-wide)
iron-rich
meteoroid struck the Earth's surface about 50,000 years ago

David Roddy, USGS.
![]()
B. Geosynchronous Orbits
1. When a satellite orbits in time with earth’s rotation it is called geosynchronous.
2. Time for
one revolution - 24 hrs
3. A satellite at distance of 6 earth radii from earth's center will orbit earth every 24 hrs.
4. Since both satellite and earth move together, it always remains directly above same spot above earth’s equator.
Meteorite Impact in Virginia
PHET Animation
Why does the moon have so many craters
compared to the earth? (Hint:
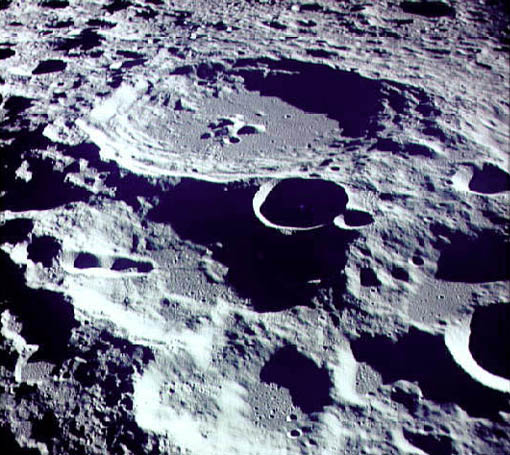

The moon has very little erosion.
"On Earth, impact craters are harder to recognize because of weathering and erosion of its surface. The Moon lacks water, an atmosphere, and tectonic activity, three forces that erode Earth's surface and erase all but the most recent impacts. Approximately 80% of Earth's surface is less than 200 million years old, while over 99% of the Moon's surface is more than 3 billion years old. Essentially, the Moon's surface has not been modified since early in its history, so most of its craters are still visible."
![]()
![]()
Learn more about Circular Motion at
Georgia Public Broadcasting
©Tony Mangiacapre., - All Rights Reserved [Home]
Established 1995
Use any material on this site (w/ attribution)

