![]()
![]()
Euler's disk
What energy change occurs below?
II. Energy (Joules)
- 2 kinds
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Potential & Kinetic Energy
A) Potential Energy - stored energy that an object has due to its position or condition.
 |
 |

 |
"At what position(s) or condition(s) do these objects have the most PE?" |
1. Gravitational P.E.g
(PE = Potential Energy)

Two factors determine PE
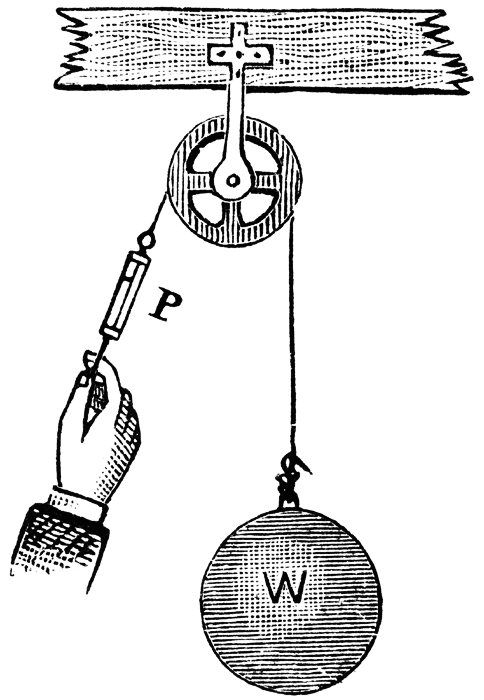
Source: Elroy M. Avery School Physics (New York: Sheldon and
Company, 1895) 141
Copyright: 2009, Florida Center for Instructional Technology. See
license.
Height, weight
| P.E.g = | (mg)h = | (weight)h |
| Joules | Kg (m/s2)m | N m |
| (Not in reference) |
g on earth = 9.8 m/s2
mg = weight
(force it could exert)

h = height
(distance force could be exerted)
| ΔP.E. | = mgΔh | = wΔh |
| (Not in reference) |
|
Ex 1) What P.E. is gained when a
100. kg object is raised 4.00 m straight up?
|
Ex 1) What P.E. is gained when a 100. kg object is raised 4.00 m straight up?
m = 100. kg
h = 4.00 m
ΔP.E. = mgΔh
= (100. kg)(9.81 m/s2)4.00 m
= 3920 J
|
Ex 2) What PE would be gained if an object were moved 4 m to the right? |
ΔP.E. = 0

|
Ex 3) An object weighing 15. N is lifted from the ground to a height of .22 m. Find object's change in PE |
Ex 3) An object weighing 15. N is lifted from the ground to a height of 0.22 m. Find object's change in PE
| ΔP.E. | = mgΔh | = wΔh |
| (Not in reference) |
w = 15. N
h = .22 m
ΔP.E. = wΔh
ΔP.E. = 15. N(.22m)
ΔP.E. = 3.3 Nm
 |
"Crow bars reduce the force needed to move a body" |
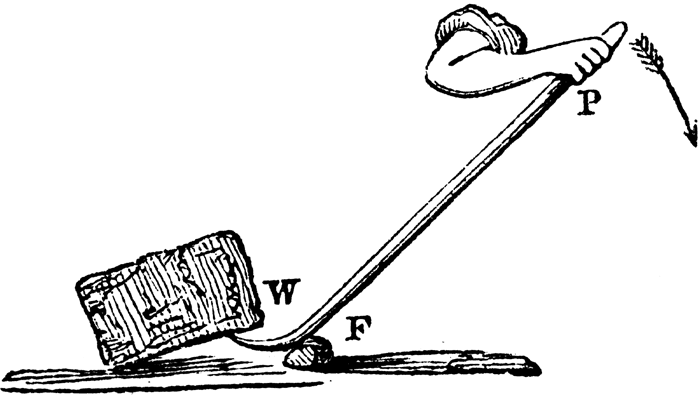
G. P. Quackenbos A.M. A Natural Philosophy: Embracing the Most Recent Discoveries in the Various Branches of Physics, and Exhibiting the Application of Scientific Principles in Every-day Life (New York: D. Appleton and Company, 1859) 95
 |
"... remember what you learned on a seesaw? " |
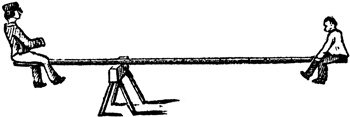
Work = DPE
W + F & D same direction
W - F & D opp. direction
Ex) A 1.60 m person lifts a 2.10 kg book from the ground to 2.20 m above the ground.
a) How much work was done lifting the book?
Work = DPE
W = mgDh
Work = 2.10kg[9.80 m/s2]2.20m
W = 4.5.3 J
c) How much W is done relative to ground? / relative to top of head/
![]()
 Elastic
PE - AP
Elastic
PE - AP
![]()
ŠTony Mangiacapre., - All Rights Reserved [Home] Established 1995
Use any material on this site (w/ attribution)
