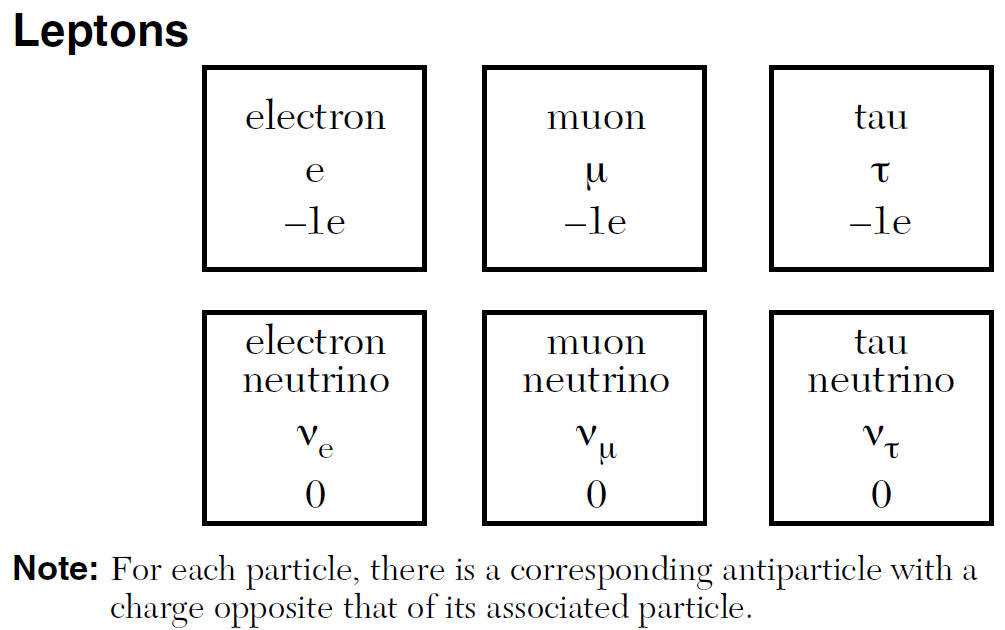
Subatomic Particles Ė particles smaller than an atom
(reference table)
(reference table)
Ex) Neutrino Ė no charge and less mass than electron!! (Travel close to speed of light!!!!)
|
Sun produces so many neutrinos
that 70 billion neutrinos
pass through every cm2 (0.15 in2) of the surface
of Earth |
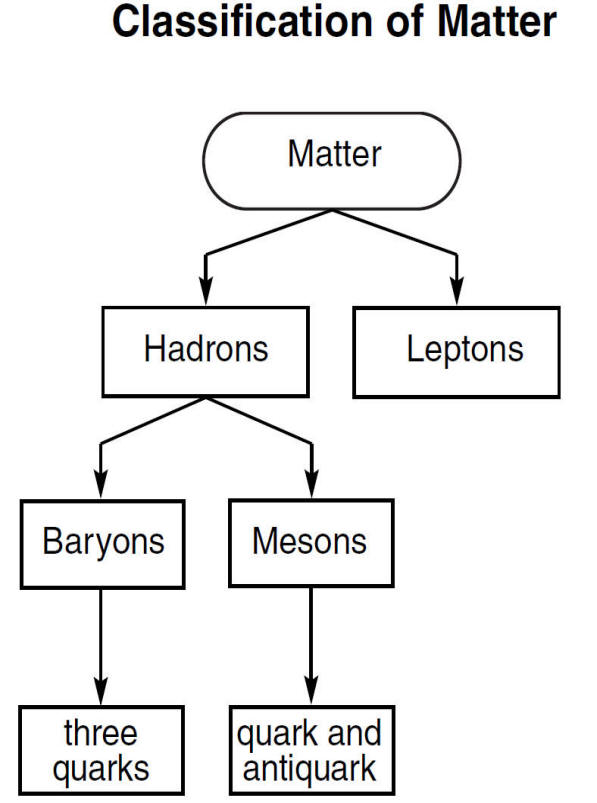
Meson Ė mass somewhere between an electron and proton
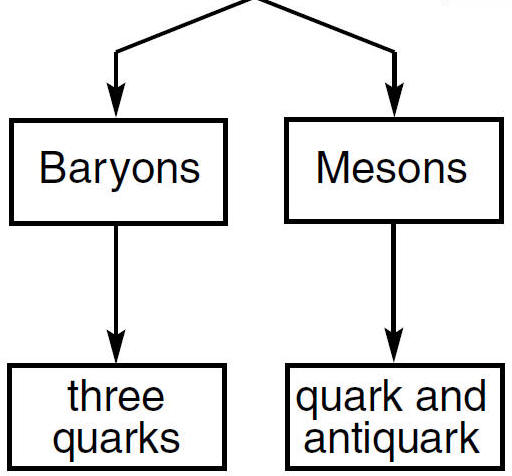
- made of a quark and an anti-quark

An electron is a lepton
Name that Nuclear Reaction!!!
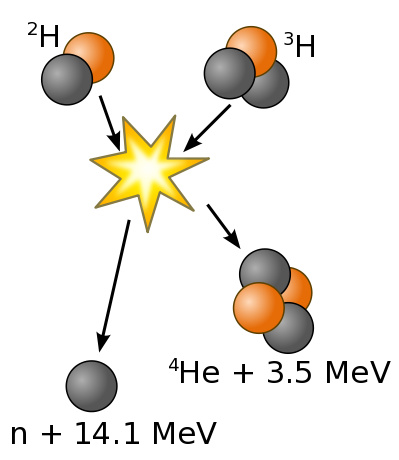
Fusion
Baryons - relatively larger subatomic particles
ex) Protons, neutrons & hyperons (mass greater than neutron)
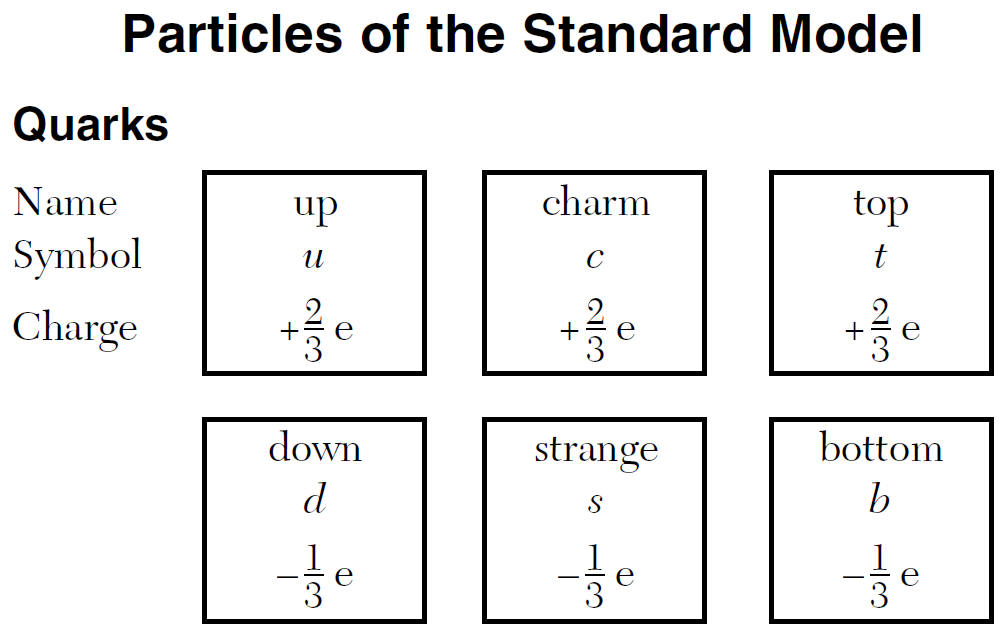
Baryons are made of smaller particles called quarks (see ref.)

| 3 Quarks make up every Baryon |
Ex 1)
A lithium atom consists of 3 protons, 4 neutrons, and 3 electrons. This atom contains a total of
a) 9 quarks
and 7 leptons
b) 12 quarks and 6 leptons
c) 14 quarks and 3 leptons
d) 21 quarks and 3 leptons


3 p and 4 n each made of 3 quarks
3 electrons, means 3 leptons
d)21 quarks and 3 leptons
Each subatomic particle
has an "antiparticle"
(same mass, opposite charge)
The ďantiparticleĒ of an electron
is called a positron
|
0 |
0 |
|||
| e | e | |||
| -1 |
+1 |
Ex 2)
During beta decay, a neutron decays into a proton, an electron, and an electron antineutrino. During this process there is a conversion of a
n --> p + e + neutrino
(1) u quark to a d quark
(2) d quark to a meson
(3) baryon to another baryon
(4) lepton to another lepton
Answer:
(3) baryon (neutron) to
another baryon (proton)
Ex 3) Which combination of quarks could produce a neutral baryon?
(1) cdt (2)
cts
(3) cdb
(4) cdu
Answer:
(3) cdb
charm +2/3
down -1/3
bottom -1/3
Sum = 0
Ex 4) Which combination of quarks would produce a neutral baryon?
(1) uud (2) udd (3) -u-ud (4) -udd
Answer:
(2) udd
up: +2/3
down -1/3
down -1/3
(Sum = 0)
What does this symbol mean?
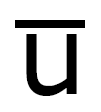
Anti Up Quark
Same size as an up,
opposite sign (-2/3)

What are we really made of?
Lyrics:
[Morgan Freeman]
So, what are we really made of?
Dig deep inside the atom
and youíll find tiny particles
Held together by invisible forces
Everything is made up
Of tiny packets of energy
Born in cosmic furnaces
[Frank Close]
The atoms that weíre made of have
Negatively charged electrons
Whirling around a big bulky nucleus
[Michio Kaku]
The Quantum Theory
Offers a very different explanation
Of our world
[Brian Cox]
The universe is made of
Twelve particles of matter
Four forces of nature
Thatís a wonderful and significant story
[Richard Feynman]
Suppose that little things
Behaved very differently
Than anything big
Nothingís really as it seems
Itís so wonderfully different
Than anything big
The world is a dynamic mess
Of jiggling things
Itís hard to believe
[Kaku]
The quantum theory
Is so strange and bizarre
Even Einstein couldnít get his head around it
[Cox]
In the quantum world
The world of particles
Nothing is certain
Itís a world of probabilities
(refrain)
[Feynman]
Itís very hard to imagine
All the crazy things
That things really are like
Electrons act like waves
No they donít exactly
They act like particles
No they donít exactly
[Stephen Hawking]
We need a theory of everything
Which is still just beyond our grasp
We need a theory of everything, perhaps
The ultimate triumph of science
(refrain)
[Feynman]
I gotta stop somewhere Iíll leave you something to imagine Read the full text here: http://www.mentalfloss.com/blogs/archives/ --brought to you by mental_floss!
Plotting Review
Why did this student only get 1 point out of 2 on his Physics Regents? 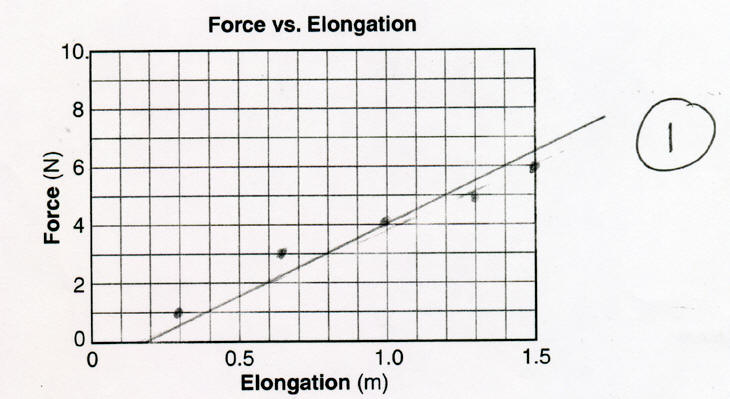 The students was under the high points and over the low points. 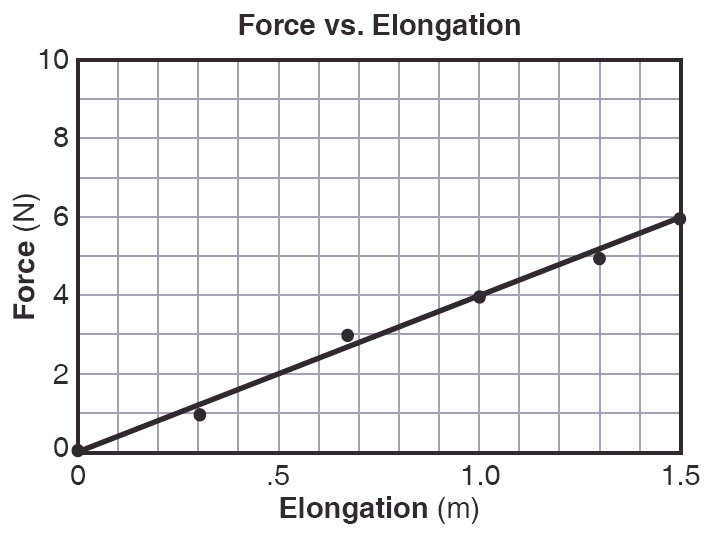 |
Identify these 4 elements
School Blocks YouTube? Use the link below.
Atomic_Spectra_of_
Various_Elements
Enrichment

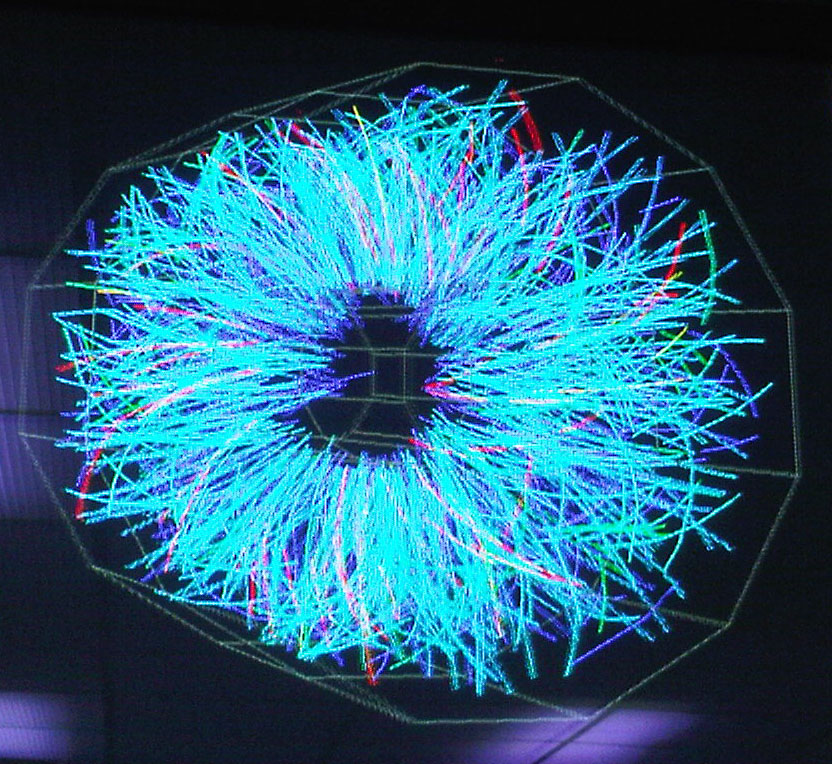
Image taken by Peggy Parigoris at Brookhaven National Laboratory.
You can learn a lot about the parts of a nucleus by creating a high speed collision between two nuclei and observing the resulting debris. Since the collision is made to occur within a magnetic field, we are able to identify the charges of the subatomic particles produced by observing the direction in which they curve.
Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider
- Analyzing the Collision Image
©Tony Mangiacapre., - All Rights
Reserved
[Home]
Established 1995
Use any material on this site (w/ attribution)