|
Intro to
Video Instruction showmethephysics.com
Unit IV - Wave Phenomena I. Introduction to Waves
Wave – a vibratory disturbance that travels through a material or space
Ex) sound, water waves, light, microwaves, heat rays |
|||||
1. Waves transfer ENERGY from one place to another with no transfer of mass 
2. Waves can be produced in two ways:
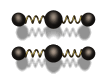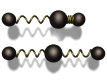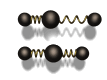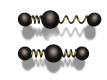
a. Vibration of particles
(requires a medium for transfer) (mechanical wave)

This movie is part of the collection: Prelinger Archives
ex) sound, water wave, spring wave
Splash of
a Water Drop
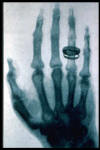
b. Small changes in the strength of an electromagnetic field (requires no medium for transfer)
ex) light, microwaves, x-rays
3d
Electromagnetic Wave
# 1 3d
Electromagnetic Wave
# 2
Radiology Centennial, Inc
How the human ear works - Biswajeet - India
©Tony Mangiacapre., - All Rights Reserved [Home] |
|||||